Wallarm Connector for Azure API Management¶
This guide describes how to secure your APIs managed by Azure API Management (APIM) using the Wallarm connector.
Overview¶
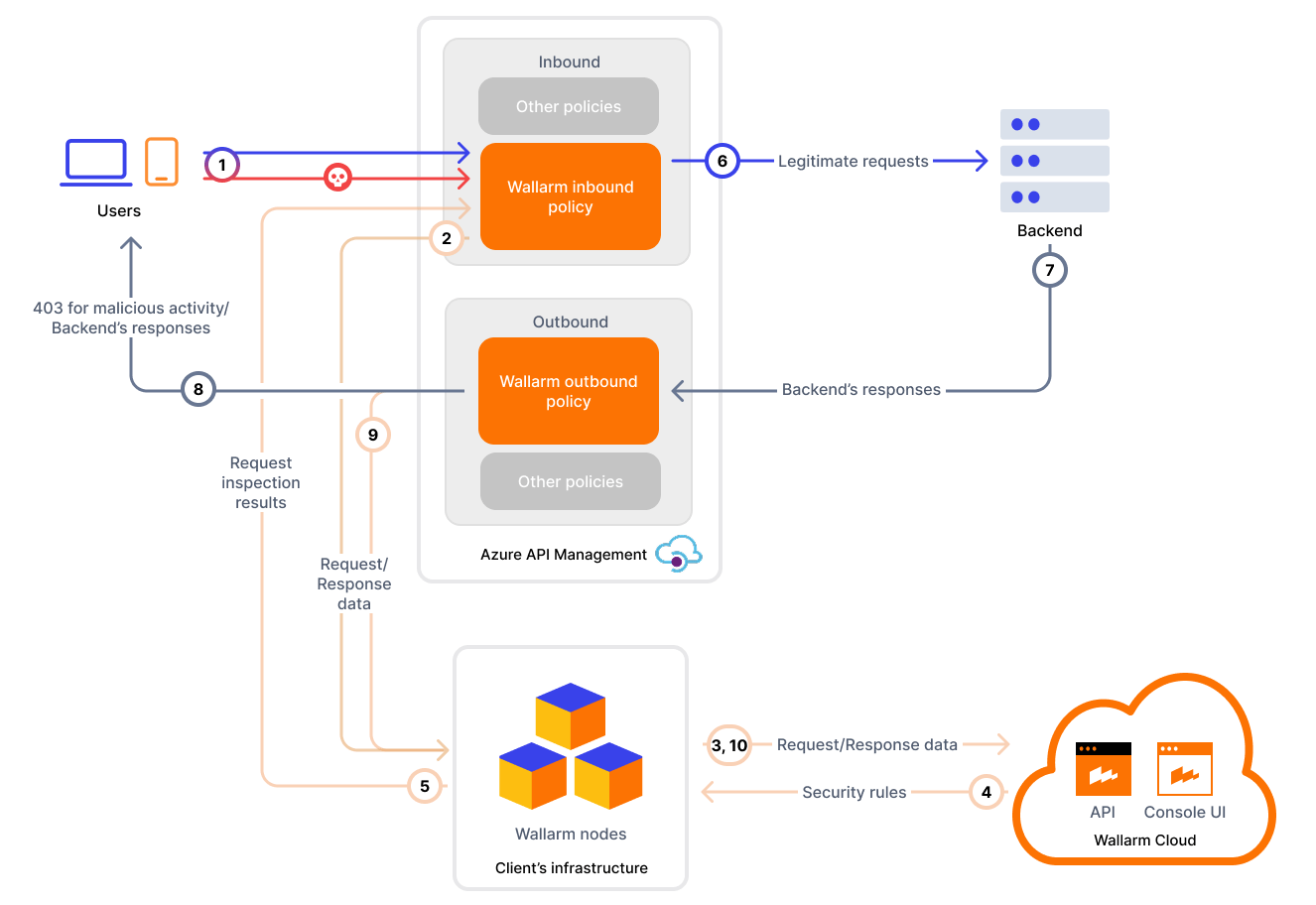
To use Wallarm as a connector for Azure APIM, you need to deploy the Wallarm Node externally and apply Wallarm policy fragments in Azure to route traffic to the Node for analysis.
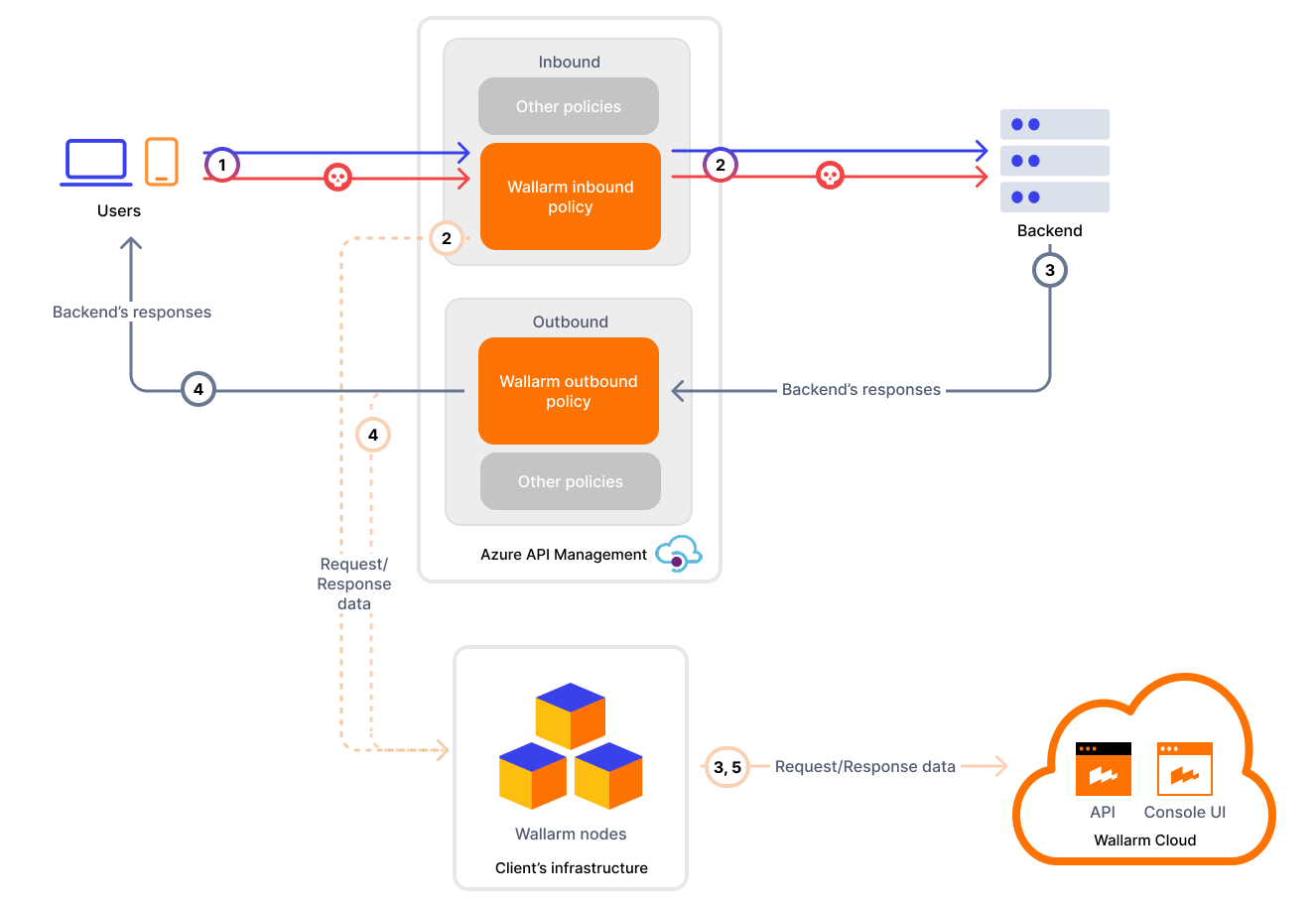
The Wallarm connector for Azure APIM supports the synchronous and asynchronous traffic analysis:
In synchronous (inline) mode, the policy intercepts requests and sends them to the Wallarm Node for inspection. Based on the Node's filtration mode, malicious requests may be blocked with 403, providing real-time threat mitigation.
In asynchronous (out-of-band) mode, traffic is mirrored to the Node without affecting the original flow. Malicious requests are logged in Wallarm Console but not blocked.
Use cases¶
This solution is recommended for securing APIs managed by the Azure APIM service.
Limitations¶
-
Custom blocking code configuration is not supported.
All blocked malicious traffic is returned with status code
403by default. You can customize the block page content, but not the response code itself. -
Rate limiting by Wallarm rules is not supported.
Rate limiting cannot be enforced on the Wallarm side for this connector. If rate limiting is required, use Azure APIM's built-in policies.
-
Multitenancy is not supported.
All protected APIs are managed under a single Wallarm account; separating protection across multiple accounts for different infrastructures or environments is not yet supported.
-
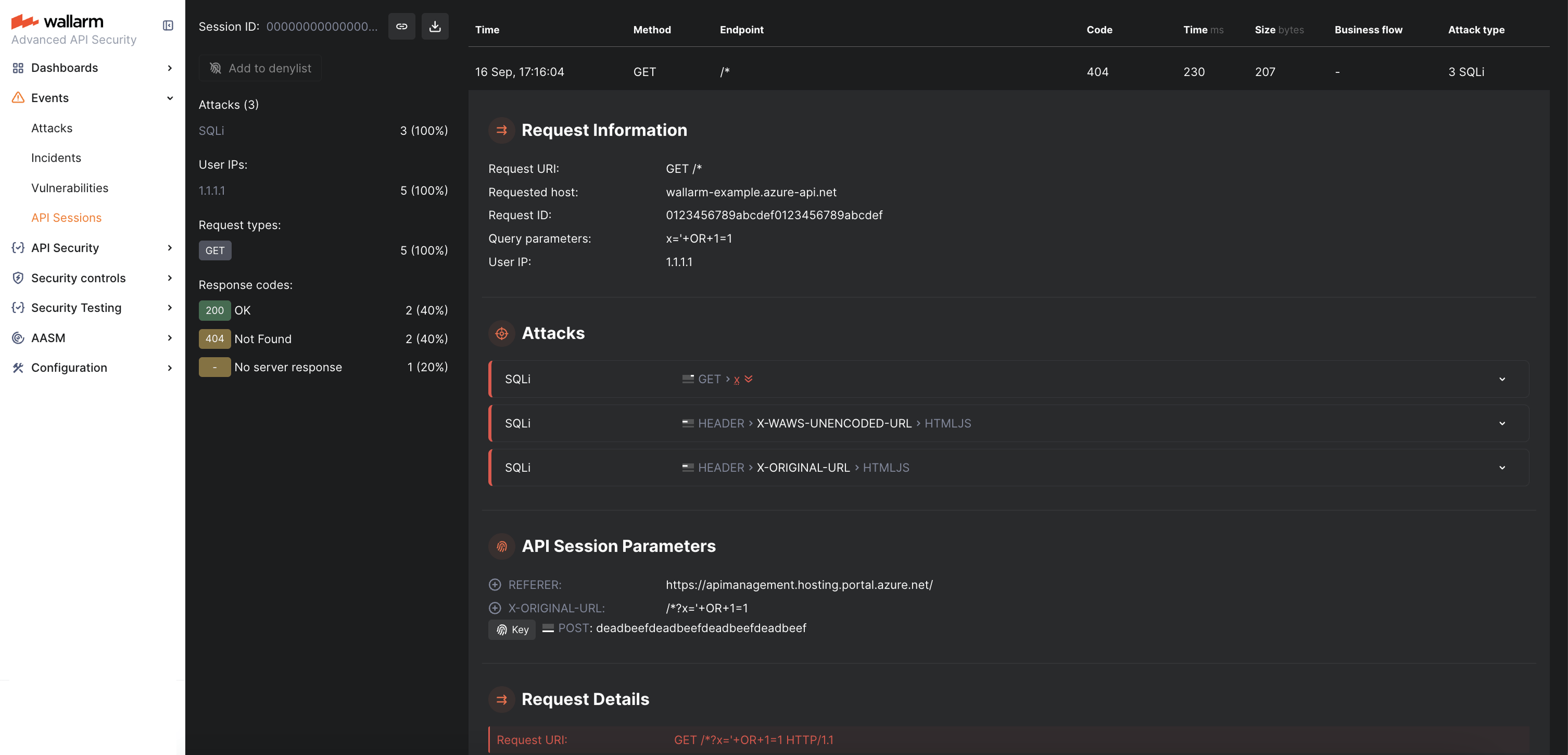
Attacks in query parameters and URI are registered 3 times.
This is because the Azure Application Gateway adds the
X-ORIGINAL-URLandX-WAWS-UNENCODED-URLheaders, which fully reflect the original URI including the attack pattern. As a result, a single malicious parameter or URI path generates three detections:- In the query parameter or URI path itself
- In the
X-ORIGINAL-URLheader - In the
X-WAWS-UNENCODED-URLheader
Requirements¶
Before deployment, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
-
Familiarity with Azure API Management.
-
APIs are published via Azure API Management.
-
A user account with one of the following roles in Azure APIM:
- API Management Workspace Contributor - for managing policy fragments within a workspace.
- API Management Service Contributor - for global configuration across the entire APIM instance.
-
Access to the Administrator account in Wallarm Console for the US Cloud or EU Cloud.
-
Native Node version 0.18.0 or higher.
-
A valid trusted SSL/TLS certificate for the Wallarm Node domain (self-signed certificates are not supported).
Deployment¶
1. Deploy a Wallarm Node¶
The Wallarm Node is a core component of the Wallarm platform that you need to deploy. It inspects incoming traffic, detects malicious activities, and can be configured to mitigate threats.
You can deploy it either hosted by Wallarm or in your own infrastructure, depending on the level of control you require.
To deploy a Wallarm-hosted node for the connector, follow the instructions.
Choose an artifact for a self-hosted node deployment and follow the attached instructions:
- All-in-one installer for Linux infrastructures on bare metal or VMs
- Docker image for environments that use containerized deployments
- Helm chart for infrastructures utilizing Kubernetes
Required Node version
Please note that the Azure APIM connector is supported only by the Native Node version 0.18.0+.
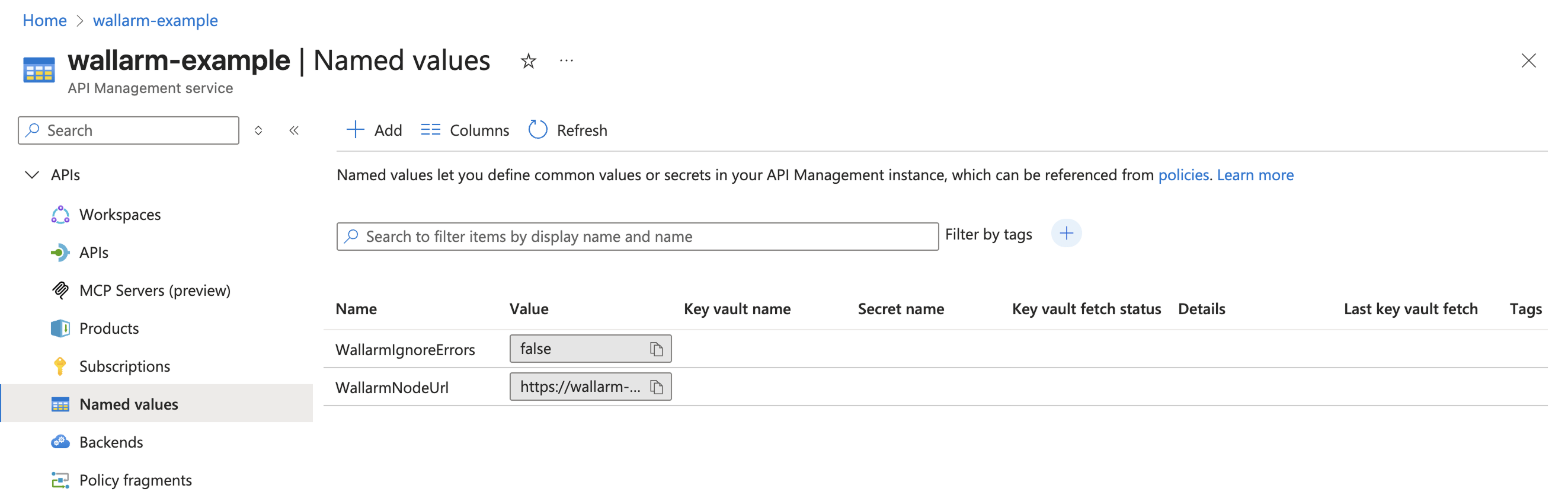
2. Create named values in Azure¶
Define the following named values in Azure API Management to reference them from policies:
| Named value | Description | Type | Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
WallarmNodeUrl | Full domain name of your Wallarm Node including protocol (e.g., https://wallarm-node-instance.com). | Plain | Yes |
WallarmIgnoreErrors | Defines error-handling behavior in synchronous traffic analysis when the Node is unavailable (e.g., timeouts):
true, meaning requests are always forwarded to APIs when the Node is unavailable. | Plain | No |
The example below shows how the named values look in the Azure Portal:
3. Obtain and deploy Wallarm policy fragments¶
The Azure API Management connector package includes 4 XML files:
-
Synchronous mode:
wallarm-inline-request.xmlwallarm-inline-response.xml
-
Asynchronous mode:
wallarm-out-of-band-request.xmlwallarm-out-of-band-response.xml
Each mode requires 2 fragments: one for requests (inbound) and one for responses (outbound).
The steps below use the Azure Portal UI, but you can also deploy policy fragments with Terraform or ARM templates.
-
Contact sales@wallarm.com to get the policy fragments.
-
Extract the policy archive.
-
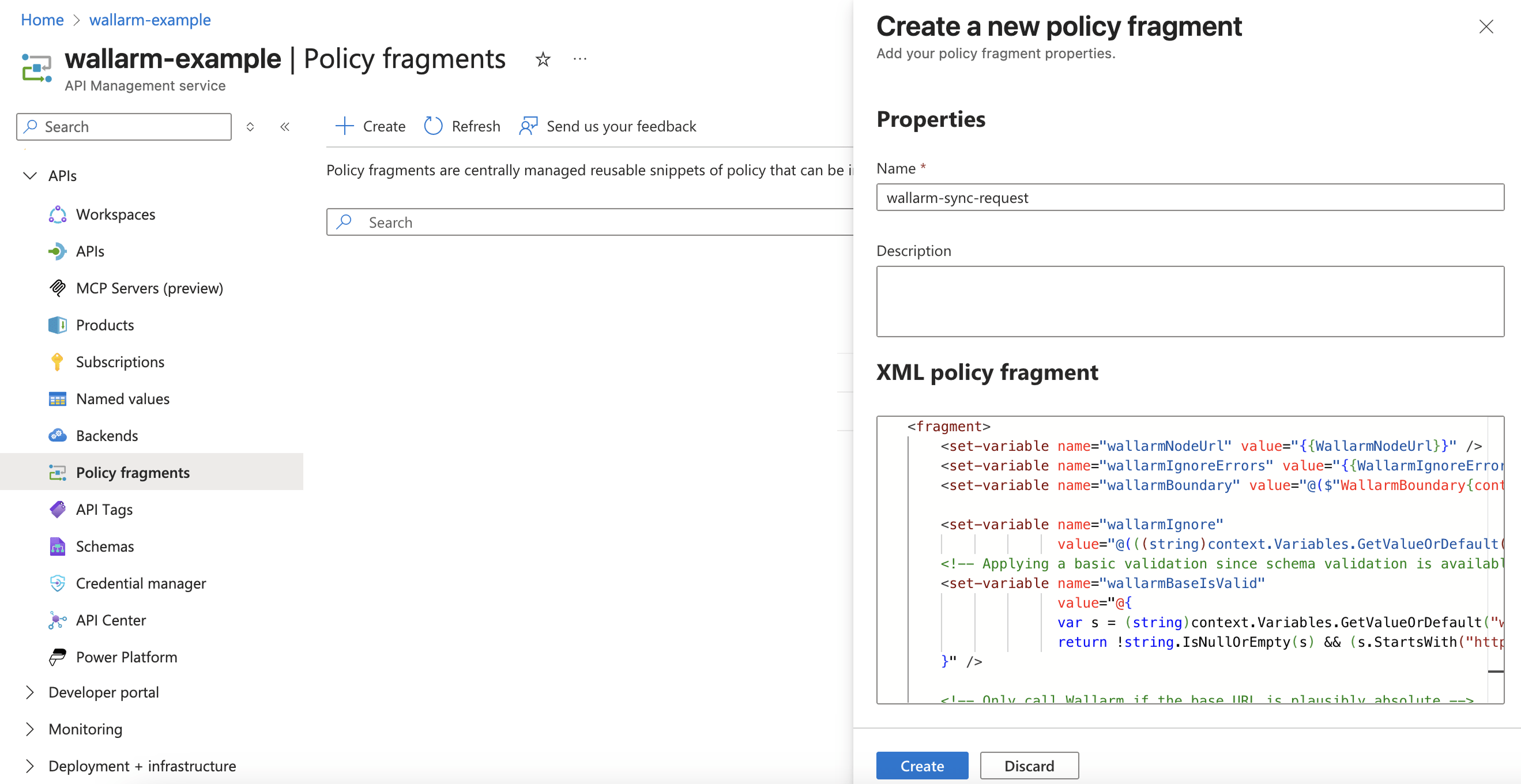
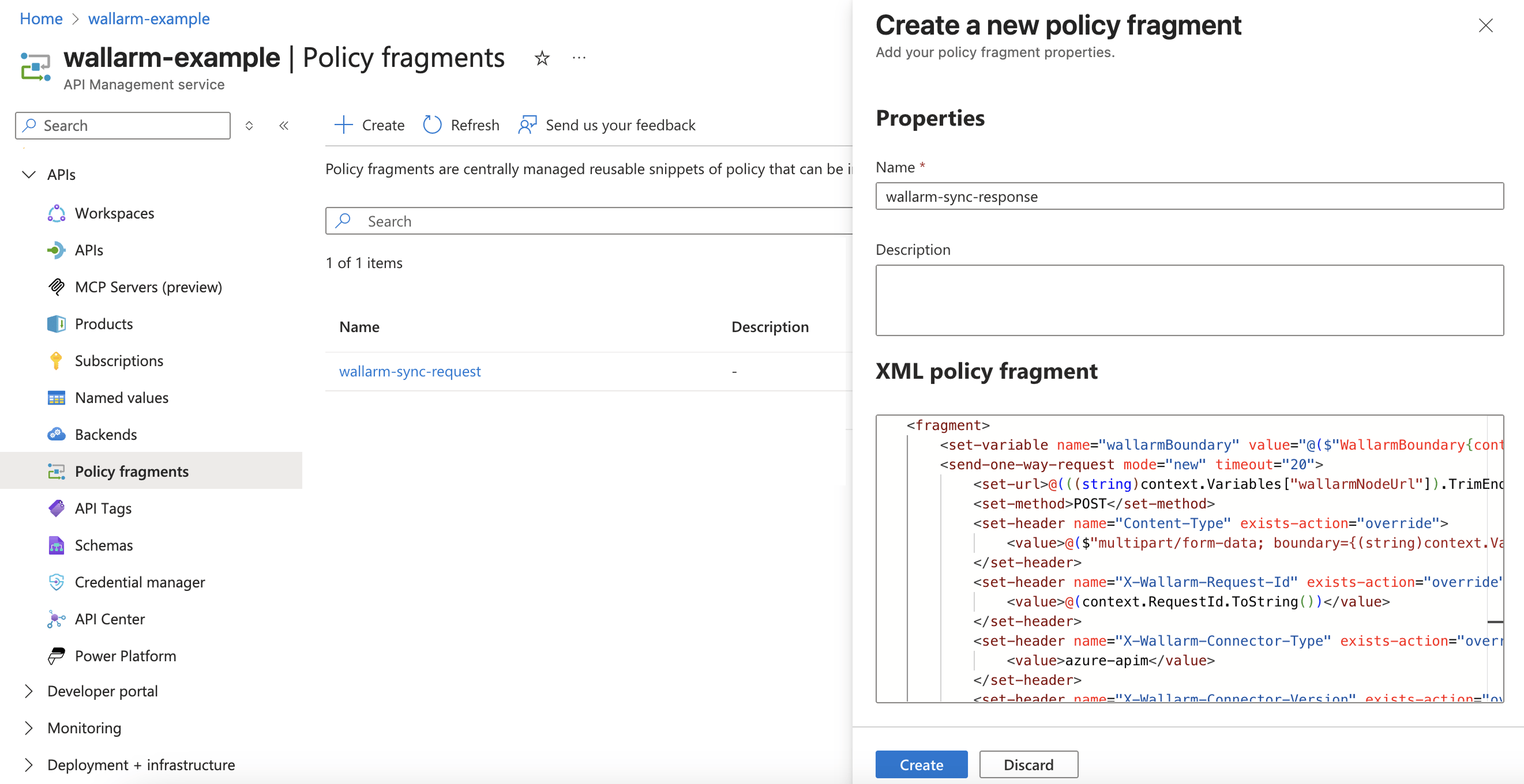
Navigate to Azure Portal → API Management service → APIs → Policy fragments → Create.
-
Create a request policy fragment using
wallarm-inline-request.xmlfor synchronous mode orwallarm-out-of-band-request.xmlfor asynchronous mode.You can name the fragment consistently with the file:
wallarm-inline-requestorwallarm-out-of-band-request.Example of a request policy fragment in Azure Portal:
-
Create a response policy fragment using
wallarm-inline-response.xmlfor synchronous mode orwallarm-out-of-band-response.xmlfor asynchronous mode.You can name the fragment consistently with the file:
wallarm-inline-responseorwallarm-out-of-band-response.Example of a response response fragment in Azure Portal:
4. Apply Wallarm policy fragments to APIs¶
You can attach Wallarm fragments globally to all APIs or individually to specific APIs or operations.
Insert fragments inside your existing policy to preserve the current flow.
Globally (all APIs)¶
-
Navigate to Azure Portal → APIs → All APIs.
-
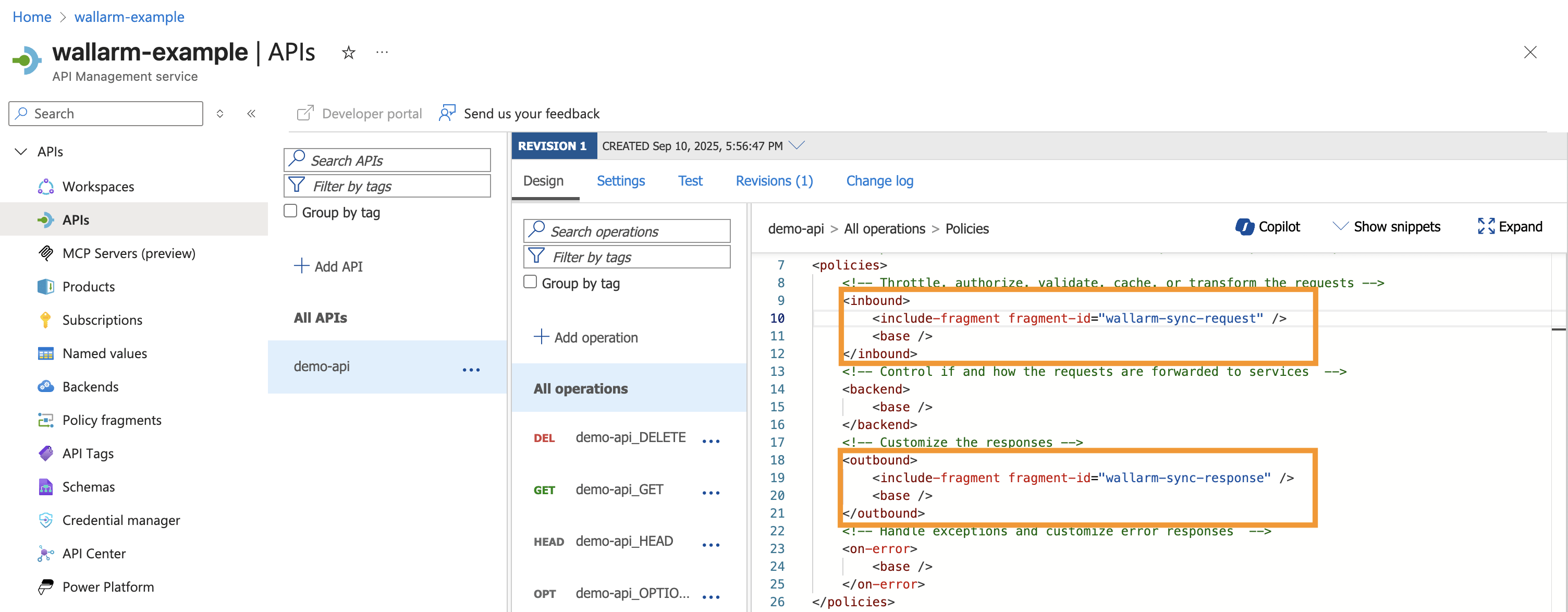
Under Inbound processing and Outbound processing, add the fragments, for example:
Per API or operation¶
To apply the created fragments to individual APIs or operations:
-
Navigate to Azure Portal → APIs → select API → All operations or specific operation.
-
Under Inbound processing and Outbound processing, add the fragments before
<base/>so inspection happens prior to routing, for example:
Example of per-API application in Azure Portal:
Testing¶
Test the deployed policy fragments with both legitimate and malicious traffic.
Legitimate traffic¶
-
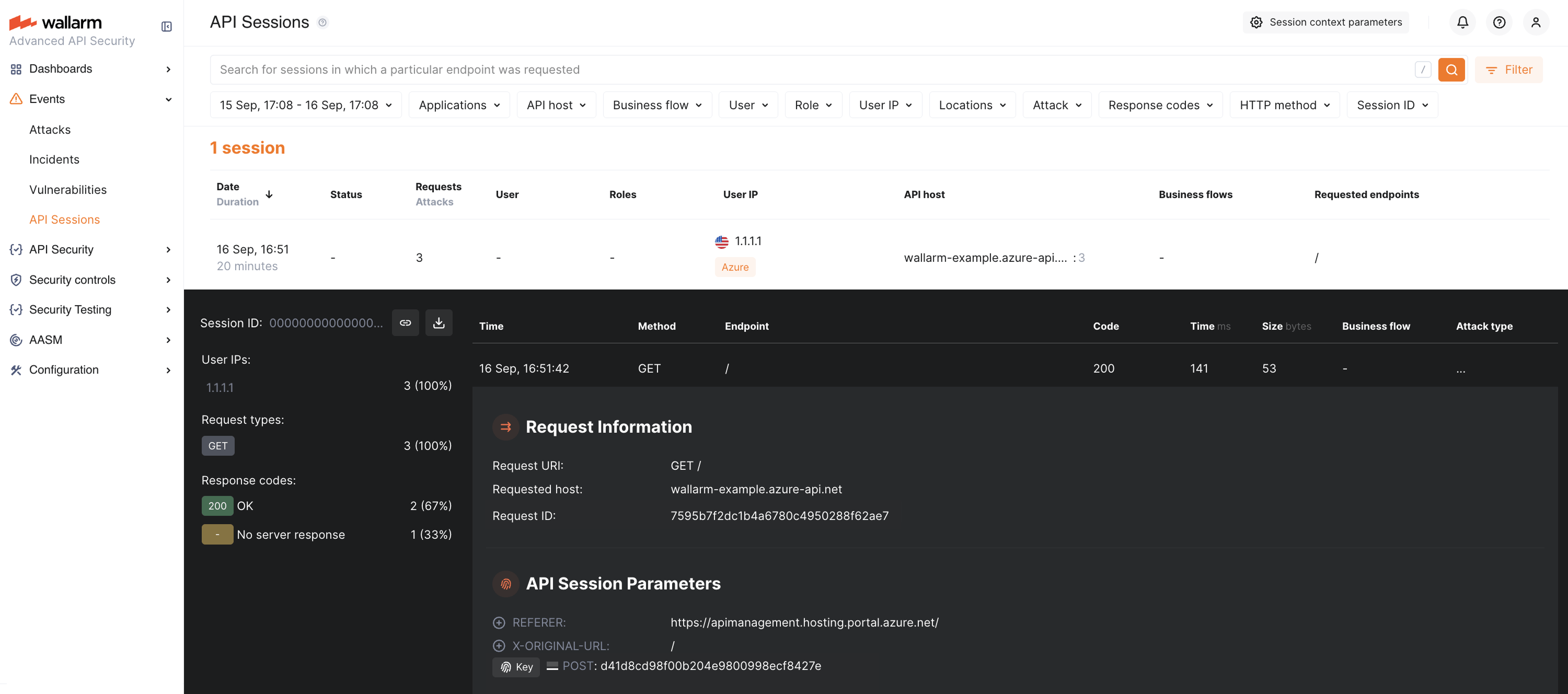
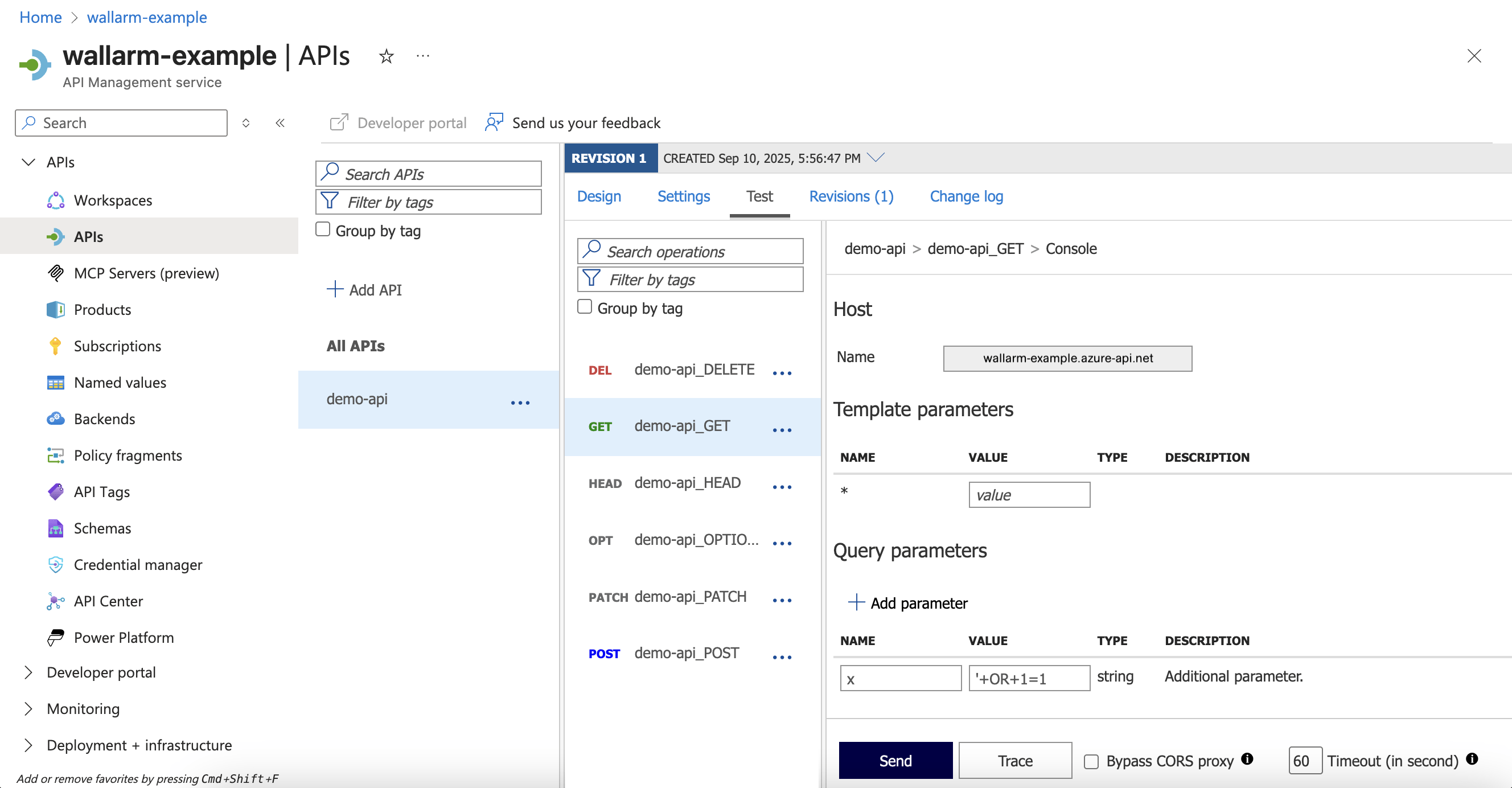
In Azure Portal, go to your API → Test → select an operation → enter valid parameters → Trace:
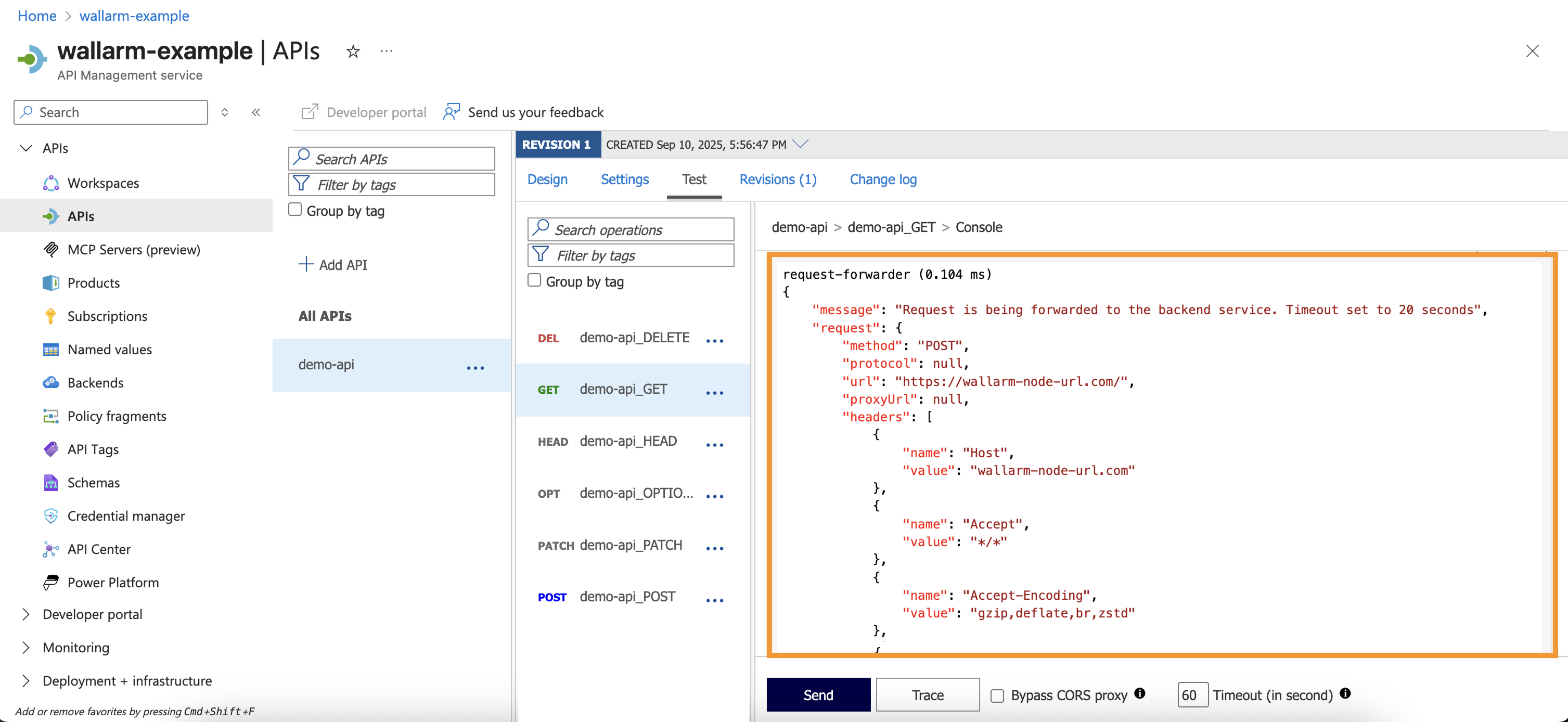
-
Review the HTTP response trace - you should see the inbound policy
request-forwarder: -
In Wallarm Console → API Sessions, verify that the legitimate request is displayed:
Malicious traffic¶
-
Send a request with a test SQLi attack by adding the query parameter
x='+OR+1=1:- Synchronous mode with blocking enabled: the request is blocked with
403. - Synchronous mode (monitoring): request reaches the API and is logged in Wallarm Console.
- Asynchronous mode: request reaches the API and is logged in Wallarm Console.
- Synchronous mode with blocking enabled: the request is blocked with
-
In Wallarm Console → API Sessions, verify that the malicious request is logged:
-
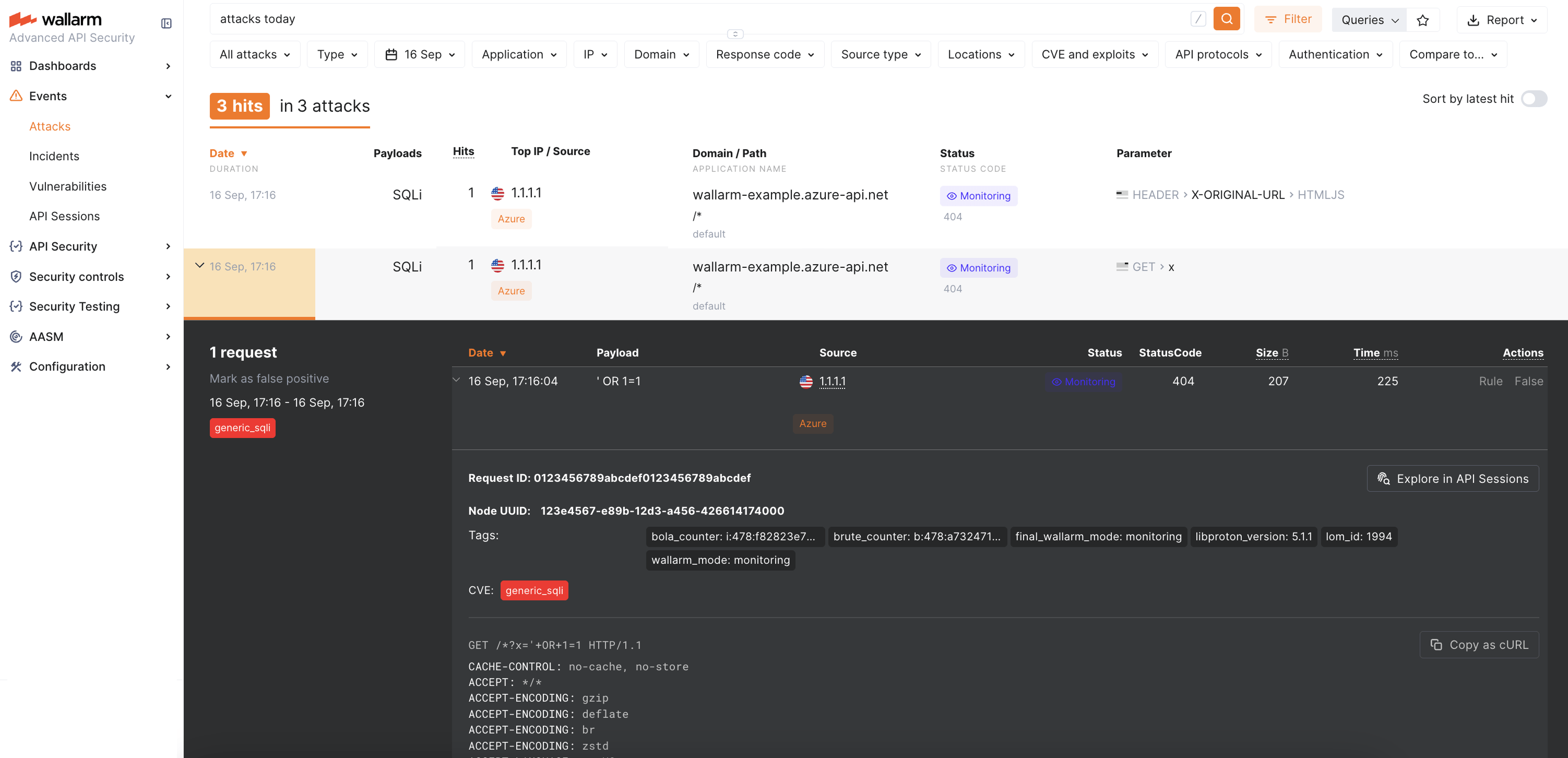
In Wallarm Console → Attacks, confirm that the attack is listed:
The attack will appear 3 times due to APIM headers.
Block page customization¶
If the Node is deployed in synchronous mode with blocking enabled, you can customize the block page returned for blocked malicious requests:
-
Navigate to Azure Portal → API Management → APIs → Policy fragments.
-
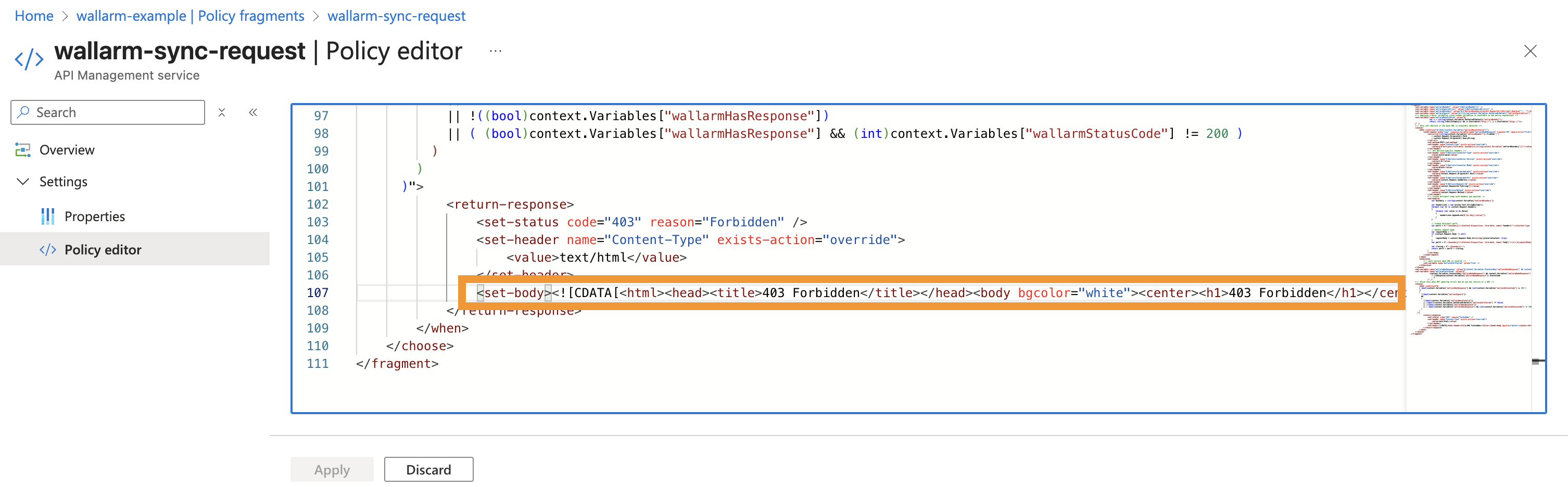
Open the
wallarm-sync-requestfragment and edit the<set-body>section:
Upgrading the policies¶
To upgrade the deployed Wallarm policies to a newer version:
-
Download the updated Wallarm policy package and create new fragments using the updated XML files, as described in Step 3.
-
Update your API policies to reference the new fragment names, as described in Step 4.
-
Test both legitimate and malicious traffic to confirm correct behavior.
Policy upgrades may require a Wallarm Node upgrade, especially for major version updates. See the Native Node changelog for the self-hosted Node release notes. Regular node updates are recommended to avoid deprecation and simplify future upgrades.
Uninstalling the policies¶
To remove the Wallarm connector from Azure API Management:
-
Navigate to Azure Portal → API Management service → APIs → your API.
-
Remove the inbound and outbound
<include-fragment>lines referencing Wallarm fragments. -
Remove the Wallarm policy fragments from Policy fragments.
-
Remove the
WallarmNodeUrlandWallarmIgnoreErrorsnamed values if they are no longer needed.